Author: linkteam
The Environmental Cost of Gold Mining
King Ferdinand of Spain, sponsor of Christopher Columbus, had only one command for the conquistadors: “Get Gold! Humanely, if possible, but at all hazards!”
500 years later this sentiment still seems to be the same, with the addition of new hazards. Gold bugs and Bitcoin advocates share the common belief that the fiat currency system is on the brink of collapse, while continuously debasing itself to stay alive. The solution? A commodity-based alternative that ensures the preservation of accrued value, impervious to debasement.
With the upcoming 4th halving of the block subsidy from 6.25 to 3.125 BTC in April 2024 the inflation rate (annual growth rate of total supply) of Bitcoin will be 0.9%. Additionally to its higher portability and divisibility than conventional gold, the “digital gold’s” inflation rate will be lower than gold’s inflation rate (~ 1.7%) and continue to drop to lower rates in the future.
But when asked for their choice of a store of value, many investors say things like:
“I’d choose gold. Not Bitcoin, because of the environment!” Really?!
Contrary to that perception, research tells us that Bitcoin mining can enhance renewable energy expansion (Bastian-Pinto 2021, Rudd 2023; Ibañez 2023; Lal 2023) and incentivize methane emission reduction (Rudd 2023, Neumüller 2023) while having half of the carbon footprint (70 Mt CO2e) of gold mining (126 Mt CO2e).
When people think of gold, they think of a pure and clean substance. The reality of gold production, however, looks very different. As I have watched environmental scientists developing water pollutant adsorbers, I have learned that gold mining is one of the most polluting industries in the world. Further digging into the topic leads to the following facts.
Gold mining ranks second after coal mining (7200 km2) in land coverage. Gold mining sites (4600 km2) cover more than the next 3 metal sites combined (copper: 1700 km2, iron: 1300 km2 and aluminum: 470 km2).
As many high yield gold mines have been exhausted, chemical processes, like cyanide-leaching or amalgamation, with extensive use of toxic chemicals are being used today. The contaminated water from gold mining called acid mine drainage is a toxic cocktail for aquatic life and works its way into the food chain.
Colorado’s Animas River turned yellow after the Gold King Mine spill of 3 million gallons of toxic waste water in August 2015. From:
In the U.S., 90% of the cyanide is used solely to recover hard-to-extract gold. The toxic material and its production and transport is in direct relationship with the gold market. It is estimated that gold mines use more than 100,000 tons of cyanide each year. That means massive production and transport of a compound with a human fatal dose of a few milligrams.
In 2000, a tailings dam at a gold mine in Romania failed and 100,000 m3 of cyanide-contaminated water went into the Danube River watershed. The spill caused a mass die-off of aquatic life in the river ecosystem and contaminated the drinking water of 2.5 million Hungarians. Mines in Brazil and China widely use the historic amalgamation method that creates mercury waste. Roughly 1 kg mercury is emitted for 1 kg of mined gold.
Gold production from artisanal and small-scale mines, mostly in the global South, accounts for 38% of global mercury emissions.
Thousands of tons have been discharged into the environment in Latin America since 1980. 15 million small scale mine workers were exposed to mercury vapor and the residents of downstream communities ate fish heavily contaminated with methylmercury.
Mercury poisoning among these populations causes severe neurological issues, such as vision and hearing loss, seizures, and memory problems. Similarly, in the townships of Johannesburg in South Africa, poor communities are paying the price for the country’s rich gold mining past.
Knowing about the risks, western mining companies have moved increasingly to developing countries as a response to stricter environmental and labor regulations at home. Surprisingly, only 7% of mined gold is used for material property purposes in industry (e.g., in electronics). The rest is processed for jewelry (46%) or directly purchased as a store of value by retail or central banks (47%). That’s why periods of high monetary debasement are boosting the price of gold. Last year central banks bought 1000 tons of bullion, the most ever recorded, while gold has been hovering close to its nominal all-time high (status: December 2023).
The last time gold demand increased its price substantially was the monetary debasement following the 2008 global financial crisis. During that time gold mining in western Amazonian forests of Peru increased by 400%, while the average annual rate of forest loss tripled.
As virtually all of Peru’s mercury imports are used in gold mining, the gold price corresponded with an exponential increase in Peruvian mercury imports.
As a result of the artisanal mercury handling, large quantities of mercury were being released into the atmosphere, sediments and waterways.
The massive mercury exposure can be detected in birds in central America. A region that supports over half of the world’s species.
Figure 1: Gold price, Peruvian mercury imports and mining area, from “Gold Mining in the Peruvian Amazon: Global Prices, Deforestation, and Mercury Imports.” 2011, PLoS ONE 6(4): e18875.
Other natural areas endowed with gold deposits like the Magadan Region in Northeast Russia are experiencing similar expanding mining activity over the past years including environmental destruction in response to high gold prices.
Gold mining, largely driven by demand for a store of value, causes widespread ecological and social harm across the world. It is the coal of value storage mediums.
At least half of today’s gold mining could be prevented by using a different store of value – a digital commodity with higher portability, divisibility and scarcity.
So, next time an environmental conscious investor argues for gold vs. Bitcoin, tell them:
A 21st century store of value should not rely on huge carved out fields of destruction and poisonous hazards but on electricity from non-rival energy, subsidizing renewable expansion.
This is a guest post by Weezel. Opinions expressed are entirely their own and do not necessarily reflect those of BTC Inc or Bitcoin Magazine.
Pricing Out Inscriptions
The battle for the future of Bitcoin is raging in real time on twitter as we are on the cusp of global economic contraction, thanks to 50+ years of the USD fiat regime, and are eagerly waiting for the approval of a spot Bitcoin ETF by the SEC. Yet, in the trenches on Twitter, the skirmish being fought is over what bitcoin is and how it should and shouldn’t be used. I covered this battle in some detail on Orange Label, but to summarize there are two camps in this battle: Monetary Maximalists & Blockspace Demand Maximalist. The big question is should inscriptions be a part of Bitcoin and how can they be stopped?
The purpose of this piece is not to sway you one way or another, but rather share some numbers that make the case that inscriptions will be priced out over time. Over the past year, we saw a doubling of BTC price and hashrate and during that time inscriptions caused some big changes in blockspace demand. We saw fees rise to a 4 year high as mempools were purging reasonable fees1, which means there were so many high fee transactions in mempools that lower fee transactions were being dropped from mempools. In other words, there was no chance for low fee transactions to be included in blocks. What started as a laughable novelty 12 months ago has brought in legions of new bitcoiners. This is an undeniable fact when you look up the number of reachable nodes on the network over the past couple years.
As bitcoin twitter has begun to divide on the topic, a meme has emerged suggesting that inscriptions will be priced out as NGU technology does its thing. This leads to the next logical question… at what point do inscriptions get priced out? That’s for the market to decide. For now, we can simply run the numbers and see how many dollars an inscription will cost as Bitcoin price appreciates.
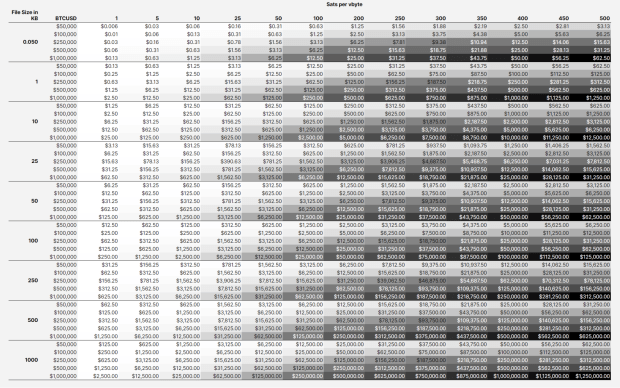
The Calculator
I am a big fan of table calculators23 and use them quite often when creating a story. For this piece I wanted to understand how much it would cost to inscribe a 100kb photograph at various prices. That then turned into asking how much these BRC20 shitcoiners are spending, and when will that nonsense end. These are around 50bytes or 0.05 kb in size for reference. I was able to track down4 a simplified formula for making an inscription:
Ordinal Inscription Cost Calculator Formula
Total USD Cost = ((((Inscription size in kb * 1000) / 4 * Fee Rate)) / 100,000,000 ) * Current BTCUSD Price
The important variables for this calculation is the file size in kilobytes, the fee rate in sats/vbyte, and the current BTCUSD price. With this little bit of information I was able to make a simple static table to see how different sized inscriptions will increase in USD cost as NGU for fees and BTCUSD.
This chart reveals much information and the big takeaway for me is just how expensive it will be to put data in blocks in the not too distant future. Let’s take our 100kb image example. At current fees around 100 sat/vbyte and $50,000 BTCUSD that will cost $1,250 to inscribe. That is a big pill to swallow. Now let’s examine the shitcoin token BRC20 that’s used for money laundering… It is around 0.05kb in size. ‘At current fees around 100 sat/vbyte and $50,000 BTCUSD that will cost $0.63 to inscribe. That is a small amount, but these things are being inscribed by the truckload. We are talking collections with 1m units. So not a small amount and there is not a single BRC20, there are tons popping up. The question about the liquidity for these things is for a different post.
As you move down the chart to higher BTCUSD prices for each inscription size, you can see just how ridiculous things become. Our humble 100kb jpg will cost $62,500 to inscribe when BTCUSD hits $1m and 200 sat/vbyte. Similarly the same BRC20 would increase to $25 for a single token. These kind of prices start to price out the really dumb like monkey pictures and memecoin shitcoins.
As you can see, these inscriptions production cost increases linearly with BTCUSD increases. This alone will price out large portions of the market, however you must ask yourself as the overall market size increases, that will bring new entrants who will drive additional demand, in other words the pond will get bigger and the fish will get bigger, the small fish just won’t get to eat.
What to expect?
Thinking through what happens next is tough, as there are many plausible outcomes but the one I am coming back to is the meme that I mentioned at the start of this article, inscriptions will be priced out. Just run the numbers, they don’t lie. I don’t think we are anywhere near inscriptions dying in the short term, but there will come a point in time where it is just too expensive for dumb things to exist on chain. Low time preference activities will prevail.
I see the overall inscription ecosystem continuing to evolve and that means people’s minds and opinions will continue to change too. We are seeing thoughtful commentary from devs5 warning6 of how changing the protocol to address or eliminate inscriptions usage will only push people to “exploit” other parts of the protocol for it’s precious blockspace. We are seeing novel new ways to crowd fund inscriptions and incentive the seeding of data via bitcoin + torrents such as ReQuest, Durabit, and Precursive Inscriptions. Inscriptions are a thing, blockspace is precious, and people are willing to pay for it. Bitcoin is for enemies, and it is going to get weird(er). Cope and seethe but remember to have fun.
Reasonable is subjective, markets clear. I believe I saw transactions with fees as high as 20 sat/vbyte being purged, which in recent memory feels absurd. ↩︎Demystifying Hashprice ↩︎Satsflow Scenarios ↩︎Someone made this and it is pretty handy. I used this formula to build out my table in google sheets. https://instacalc.com/56229 ↩︎“Concept NACK.
I do not believe this to be in the interest of users of our software. The point of participating in transaction relay and having a mempool is being able to make a prediction about what the next blocks will look like. Intentionally excluding transactions for which a very clear (however stupid) economic demand exists breaks that ability, without even removing the need to validate them when they get mined.
Of course, anyone is free to run, or provide, software that relays/keeps/mines whatever they want, but if your goal isn’t to have a realistic mempool, you can just as well run in -blocksonly mode. This has significantly greater resource savings, if that is the goal.
To the extent that this is an attempt to not just not see certain transactions, but also to discourage their use, this will at best cause those transactions to be routed around nodes implementing this, or at worst result in a practice of transactions submitted directly to miners, which has serious risks for the centralization of mining. While non-standardness has historically been used to discourage burdensome practices, I believe this is (a) far less relevant these days where full blocks are the norm so it won’t reduce node operation costs anyway and (b) powerless to stop transactions for which an existing market already exists – one which pays dozens of BTC in fee per day.
I believe the demand for blockspace many of these transactions pose is grossly misguided, but choosing to not see them is burying your head in the sand.” – Peter Wuille Link ↩︎“Ever since the infamous Taproot Wizard 4mb block bitcoiners have been alight, fighting to try and stop inscriptions. Inscriptions are definitely not good for bitcoin, but how bitcoiners are trying to stop them will be far worse than any damage inscriptions could have ever caused.” – Ben Carman Link ↩︎
Bitcoin Surpasses Silver To Become Second Largest ETF Commodity In The US
Bitcoin exchange-traded funds (ETFs) have surpassed silver ETFs in the United States, securing their position as the second-largest ETF commodity, in terms of assets under management (AUM). The surge in popularity of Bitcoin ETFs signals a growing acceptance of BTC as a mainstream investment vehicle.
As reported by The Block, Bitcoin’s ascent to becoming the second-largest ETF commodity in the U.S. marks a significant milestone for the Bitcoin market. This achievement is attributed to the increasing demand from institutional and retail investors seeking exposure to BTC.
Silver, which has ~$11.5 billion in AUM across five silver ETFs, was passed by spot Bitcoin ETFs which now hold over $28 billion, less than a week after going live.
“Bitcoin ETFs have exceeded silver ETFs in the U.S. in terms of size, driven by the substantial market interest they have received,” Bitfinex Head of Derivatives Jag Kooner told The Block. “The level of trading reflects the pent-up demand for these products, and we expect that it will lead to increased liquidity and stability in the market.”
This development is particularly noteworthy given silver’s traditional status as a prominent commodity investment. The rise of Bitcoin ETFs to the second position underscores Bitcoin’s maturation within the financial markets, gaining credibility and recognition as a formidable investment option.
Investors’ growing appetite for Bitcoin ETFs reflects a broader trend of diversification within portfolios and a recognition of the unique value proposition offered by BTC. As the Bitcoin market continues to evolve, the achievement of surpassing silver ETFs solidifies Bitcoin’s position as a major player in the global financial landscape.
Don’t Break Userspace!
“Mauro, SHUT THE FUCK UP!It’s a bug alright – in the kernel. How long have you been a maintainer? And you *still* haven’t learnt the first rule of kernel maintenance?If a change results in user programs breaking, it’s a bug in the kernel. We never EVER blame the user programs. How hard can this be to Understand?” -Linus Torvalds
Don’t break userspace. This is Linus Torvald’s golden rule for development of the Linux kernel. For those of you reading this who are not familiar with the nature of Linux, or operating systems in general, the kernel is the heart and soul of an operating system. The kernel is what actually manages the hardware, moving bits around between storage and RAM, between the RAM and the CPU as things are computed, and all of the little devices and pieces of the actual computer that need to be controlled at the hardware level.
Every application or program written for an operating system has to interact with the kernel. When you download Photoshop, or Telegram, everything that program is doing boils down to essentially calling the kernel. “Hey kernel, take what I just typed and process it and send it over a network connection to the server.” “Hey kernel, take the color shift I made to this pitch, take it out of RAM and send it to the CPU to modify it, then put it back in RAM.”
When the kernel is changed, in a somewhat similar fashion to Bitcoin, the chief goal of developers is to ensure that existing applications that assume a specific way to interact with the kernel do not break because of a change to the kernel. Sounds very familiar to Bitcoin and the necessity to maintain backwards compatibility for network consensus upgrades doesn’t it?
“Seriously. How hard is this rule to understand? We particularly don’t break user space with TOTAL CRAP. I’m angry, because your whole email was so _horribly_ wrong, and the patch that broke things was so obviously crap. The whole patch is incredibly broken shit. It adds an insane error code (ENOENT), and then because it’s so insane, it adds a few places to fix it up (“ret == -ENOENT ? -EINVAL : ret”).
The fact that you then try to make *excuses* for breaking user space, and blaming some external program that *used* to work, is just shameful. It’s not how we work.Fix your f*cking “compliance tool”, because it is obviously broken. And fix your approach to kernel programming.” -Linus Torvalds
Linux is one of the most important, if not the most important, open source project in the entire world. Android runs on Linux, half of the backend infrastructure (if not way more) runs on Linux. Embedded systems controlling all kinds of computerized things in the background of your life you wouldn’t even consider run on Linux. The world literally runs on Linux. It might not have taken over the desktop as many autistic Linux users wanted to see happen, but it quietly ate almost everything else in the background without anyone noticing.
All of these applications and programs people use in the course of their daily lives depend on the assumption that Linux kernel developers will not break backwards compatibility in new versions of the kernel to allow their applications to continue functioning. Otherwise, anything running applications must continue using older versions of the kernel or take on the burden of altering their applications to interact with a breaking change in the kernel.
Bitcoin’s most likely path to success is a very similar road, simply becoming a platform that financial applications and tools are built on top of in such a way that most people using them won’t even realize or consider that “Bitcoin ate the world.” In a similar vein to Linux, that golden rule of “Don’t break userspace” applies tenfold. The problem is the nature of Bitcoin as a distributed consensus system, rather than a single local kernel running on one person’s machine, wildly changes what “breaking userspace” means.
It’s not just developers that can break userspace, users themselves can break userspace. The entire last year of Ordinals, Inscriptions, and BRC-20 tokens should definitively demonstrate that. This offers a very serious quandary when looking at the mantra of “Don’t break userspace” from the point of view of developers. As much as many Bitcoiners in this space do not like Ordinals, and are upset that their own use cases are being disrupted by the network traffic Ordinals users are creating, both groups are users.
So how do developers confront this problem? One group of users is breaking userspace for another group of users. To enact a change that prevents the use of Ordinals or Inscriptions explicitly violates the mandates of don’t break userspace. I’m sure people want to say “Taproot broke userspace!” in response to this dilemma, but it did not. Taproot activation, and the allowance for witness data to be as large as the entire blocksize, did not break any pre-existing applications or uses built on top of Bitcoin. All it did was open the door for new applications and use cases.
So what do we do here? To try and filter, or break by a consensus change, people making Inscriptions or trading Ordinals is to fundamentally violate the maxim of “don’t break userspace.” To do nothing allows one class of users to break the userspace of another class of users. There is fundamentally no solution to this problem except to violate the golden rule, or to implement functionality that allows the class of users’ whose userspace is broken now to adapt to the new realities of the network and maintain a viable version of their applications and use cases.
Not breaking the userspace of Bitcoin is of critical importance for its continued success and functionality, but it is not as simple as “don’t change anything.” Dynamic changes in user behavior, that require no change to the actual protocol itself, can have the same effect at the end of the day as a breaking change to the protocol. Are developers supposed to pick and choose which applications’ userspace is broken to maintain that of another application? I would say no, and go further to say that anyone advocating for such behavior from developers is demanding them to act irresponsibly and in a way that harms users of the system. So what is the answer here?
There is no answer except to push forward and continue adding improvements to the protocol that allow applications being broken by the behavior of certain users to function in the presence of emergent changes in users’ behavior. Otherwise, you are asking developers to throw out the golden rule and effectively play kingmakers in regards to what use cases are viable to build on top of Bitcoin.
If we go down that road, then what are we actually doing here? I can’t tell you what we’re doing at that point, but I can tell you it’s not building a distributed and neutral system anymore.
Instant Settlement Series: The Publishing Industry
The challenges associated with physical work and delayed payments, as discussed in the construction and logistics industries articles, might not be as directly applicable to industries with less physical movement. However, the principles of instant settlement and the removal of intermediaries can still bring efficiency and innovation to various sectors. The advantages of instant settlement, such as reduced transaction fees, faster payment processing, and increased transparency, can positively impact industries beyond the physical realm. Whether it’s in the realm of digital services, intellectual property, or other sectors that are already dematerialized, the application of instant settlement principles can streamline transactions and enhance overall efficiency.
Navigating The Written Odyssey
Entering the realm of book publishing, especially for a debut author, is a journey filled with challenges. The primary hurdle involves persuading a publishing house to forge a deal, a daunting task for those yet to establish their reputation in the market. The negotiation landscape is complicated by endless uncertainties, making it difficult to strike a mutually beneficial deal. Even if you try to be fair for both sides it is hard. Most people will prioritize themselves and what they get in an uncertain environment – like figuring out how many books will be sold for a first time author. The dynamics intensify when publishing houses provide editors to authors–an arrangement that frequently sparks friction. Authors, protective of their creative work, may resist alterations, but editors, with seasoned expertise, have to navigate the delicate balance between preserving the author’s vision and refining the content.
The complexities extend to the business side, with potential pitfalls surrounding signing bonuses. Questions linger: What if the bonus overshoots and the book underperforms? What if the book succeeds, but the bonus proves inadequate, leading the author to seek alternatives for subsequent works? Marketing poses another challenge, raising dilemmas about investments, audiobook adaptations, navigating royalty payments, and banking fees for small markets and international payments.
Just like in the logistics industry here with royalties, we have the same problem of counterparty risk. In addition to stopping the payments to the authors completely, do you trust the publishers that they are giving the correct sales numbers? Translation decisions add another layer, raising queries about language choices, and fair compensation for translators. What about the illustrators? Each party involved creates more and more friction in the system just because everyone is seeking fair compensation. The payment system does not allow them to focus on what they provide in terms of value, but focuses everyone on mitigating the shortcomings of it. Addressing these multifaceted challenges requires not only innovation but also transparent and adaptive contractual frameworks to foster a more equitable and efficient publishing ecosystem.
The challenges for authors extend beyond the realm of creative content, and the intricacies of the publishing and marketing landscape. While the invention of ebooks has somewhat dismantled barriers, enabling easier self-publishing, the journey is not without hurdles. Authors opting for self-publishing must navigate the complexities of setting up accounts and managing distribution before reaching the point of uploading their work. Once published, the dual role of author and marketer emerges, demanding not only literary prowess but also strategic promotional efforts to capture the audience’s attention and drive sales. The demanding nature of marketing leaves authors with limited time for their core competency – writing – which hinders the development of subsequent books that they would like to write.
Lighting Up Publishing: From Solo Authors to Collaborative Ventures, Unleashing the Potential of Instant Split Payments
Now that this is the third industry that we are looking into, we know that delayed payments are the problem and that they are tied to time and not actual work – “You have to write the book till this date or else…” “We will gather all payments and royalties will be paid later”. Since we know now that the Lightning Network can fix this let’s dig into the solution and what it may look like.
If you’re a first-time author and choose to publish your book on your self-made app, you can instantly receive 100% of the income for each purchase. By utilizing a non-custodial solution like Breez, where no one holds money for others, you avoid the complexities associated with traditional payment methods. This setup eliminates the need for currency exchanges, providing a seamless global payment network directly connected to your app. The benefits go beyond mere currency considerations, freeing buyers from the hassle of exchange rate fees and relieving them of the complexities associated with navigating diverse regulations and processes across various countries. Who knows what regulations you have to deal with to be able to operate with the Iranian Rial just to sell a simple book? With a non-custodial solution on the Lightning Network, you get to avoid all that.
That is a big benefit for one-man shows in the book industry, but let’s take it a step further. In this scenario, where the relationship involves only the author and a publisher, the process becomes streamlined without the need for intricate negotiations, personal data sharing, or complex contracts with various clauses. With the instant settlement, there’s no need for advance payments, both the author and publisher receive a percentage from each sale instantly when the purchase is made. The publisher, responsible for uploading and promoting the book on their website, and the author are now aligned in the common goal of selling more books. The only task left is to determine the fair percentage splits between the author and the publisher, fostering a collaborative and efficient partnership. Now the word royalties will have a completely new meaning.
Okay, that is between two entities, but we are not going to stop there. Now that the book is published the book can be translated to other languages. In that case, the complexity does not increase a lot. They just have to determine the percentage share split between the publisher, author, and translator for each sale of the translated version. Upon purchase of the translated book, each payment will be split three ways. Meanwhile, the original language version undergoes a two-way split, with the translator excluded from this split since they didn’t contribute to that version. This ensures that the relevant individuals receive sats exclusively for their specific contributions. There might be a need for a separate publisher for the translated language, leading to a split between the author, translator, and second publisher. For the original language, the split occurs between the author and the first publisher. Theoretically, the current system goes through a similar structure for the payments, but I am reminding you here that only the instant split settlement makes that plan match the reality in practice. The moment that any entity starts holding funds for someone else even for a little, then the problems go up exponentially. This is why Breez is committed to preserving the peer-to-peer nature of Bitcoin in lightning payments.
Instant Splits For Narrators, Producers, And All Contributors – A Symphony Of Fair Compensation
We are not done yet with the benefits. Now that we have a path for each language, what will it look like for audiobooks? In that case, you just add one more split based on the agreement between the parties. If you create an audiobook in the original language then the split will be between Author, Publisher, and Audiobook creator. The creation of an audiobook is a project on its own of casting, recording, post-production, and distribution. That has multiple people involved so the split for the audiobook payment in reality may look like this:
Author, Publisher, Producer, Recording engineer, Narrator, Editing/mastering engineer.
In this dynamic model, contributors may wear multiple “hats” within a project, allowing them to assume various roles and, consequently, earn a share for each responsibility they undertake. For instance, an Author might take on the roles of both Producer and Narrator, performing additional work beyond their original scope. In such cases, the Author receives a percentage for each distinct role. However, should the Author choose not to take on these additional roles, someone else can assume those responsibilities and reap the corresponding benefits. This structure ensures alignment, with compensation tied directly to individual contributions at the time of each book sale, eliminating compensation for time or speculation based on future sales.
Unlike the other two industries we explored in construction here and logistics here, the timing of payment in the publishing industry differs. In the preceding sectors, individuals receive compensation instantly upon completing their respective tasks. However, in the realm of authors, payment is not immediate for the act of writing; it occurs when someone is willing to pay the price for the published work. This distinction highlights a fundamental principle: everyone is remunerated when they deliver value to someone else who is willing to pay. Whether delivering a package to the correct address or constructing a house for someone else to inhabit, optimizing the process with the client in mind becomes paramount. Therefore, receiving sats is contingent on providing intrinsic value to others, aligning the industry with similar principles observed in construction and logistics. If you build or deliver something that people do not want, that means you did not provide value.
Instant Influence: From Metrics To Value – A Paradigm Shift In Compensation For Promotions
Now let’s take it even a step further. This will not be the only industry where the influencers can change their business model, but I will use it as an example to explain the change that they will experience in their service. Currently, the influencers get paid for views or mentions depending on whether the medium is audio or video. Their value, as perceived by those paying them, hinges on metrics such as subscriber counts, views, and downloads. But for the person that is paying, is it going to matter if the influencer talks about a book but then it does not result in sales of the book? Or again what happens if someone mentions it but the sales are extraordinary, then the influencer has to receive a more fair compensation. Connecting payments directly to actual value, rather than relying on derivative indicators, ensures influencers receive fair compensation in line with their impact on sales.
Well, the instant settlement fixes that. Authors can now decide on a fixed percentage for influencers per sale, allowing anyone to become an influencer without the need for a massive following. Even a small blog with a modest readership of less than fifty people can result in direct, instant compensation for sales generated. This eliminates barriers to entry for the influencers to have a following and aligns incentives for authors seeking broader promotion. There is a massive friction in the influencer market currently because with poor measuring tools you do not want the money to be wasted on promotion that does not work. This future system is not going to waste a single sat for promotion because it is not paying for a promotion. You are negotiating a commission on every sale which the actual buyer pays – increasing sales is the intent of the authors reaching out to influencers anyway.
Now that we have an influencer promoting a book the UX (user experience) is going to be completely different. Right now to promote anything as an influencer you receive a code that you have to ask for, from the publisher in this case. Then your viewers/listeners have to go to the website and fill in all the information about themselves. Then they have to enter their card information which has to be secured from the website somehow. Then they enter the promo code and receive the ebook that they wanted. On the other side, the publisher has to hope he does not get a chargeback for whatever reason in the next 30 days. The instant settlement UX will be:
– Influencers enter a lightning address where they want to receive their commissions from for every sale.
– Then they display a link or a QR code that will be a lightning invoice for the specific book.
– The buyer enters an email where they want the ebook to be sent.
The instant split payment is sent and everyone including the influencer receives their share of it. This way even influencers might realize that the likes, views and comments are not the most important thing and focus on providing real value for their viewers. This not only streamlines the process but may also alleviate the impact of negative comments and dislikes for influencers. Because their income is not tied to the likes that means it will no longer be the most important thing. They will focus on promoting quality products that sell a lot so they get a piece of those sales and the likes will be secondary.
The transformation in influencer behavior triggered by instant settlement not only disrupts their traditional approaches but sparks competition among publishers and influencers alike. Authors may opt for a model where they focus solely on writing, leveraging influencers to handle promotion without dealing with traditional editors. This introduces a more diverse competitive landscape, where publishing houses will compete with content creators from different industries who passionately recommend authors they love. While these changes benefit readers, authors, and participants, those resistant to competition may be the only ones disliking this evolving landscape.
Indeed, envisioning the transformative power of instant payments, there’s an opportunity for an innovator to replicate what Amazon did to bookstores. By adopting a model built on advanced technology and leveraging the advantages of instant settlements, this individual can start with books and subsequently explore avenues for expansion. The potential for such a disruptive force lies not only in reshaping the publishing landscape but also in inspiring new possibilities across diverse industries.
Now let’s go and publish that app.
This is a guest post by Ivan Makedonski. Opinions expressed are entirely their own and do not necessarily reflect those of BTC Inc or Bitcoin Magazine.
Bitcoin’s Future Is Fractional Reserve: Unless We Do Something About It
What started as a single transaction from Satoshi to Hal Finney, has evolved into a complex system of industrial scale miners, evolving meta-protocols like the Lightning Network and Fedimint, and a full embrace of institutional investors with the record breaking inflows into various newly approved spot ETFs.
Bitcoin has come a dramatically long way, and with that comes a somewhat earned sense of optimism for those who have invested their time, money, and enthusiasm.
Unfortunately this optimism, and sense of “inevitability” I have previously written on, has contributed to a culture of complacency. This is hallmarked by a narrative that early Bitcoin protocol ossification is acceptable or even desirable, itself underscored by the implicit assumption that the largest risks to Bitcoin now are potential changes and Trojan horses to the protocol.
This belief is categorically false.
The greatest danger to Bitcoin is the certain future it has if it were in fact to effectively “ossify” today: Certain regulatory capture, an uncapped fractional reserve supply, and censored and monitored transactions.
Old News
If that sounds extreme, then you haven’t been paying attention. The problems facing Bitcoin that lead to this inevitable result aren’t remotely new. In fact it was touched on by Hal Finney himself 14 years ago:
“Actually there is a very good reason for Bitcoin-backed banks to exist, issuing their own digital cash currency, redeemable for bitcoins. Bitcoin itself cannot scale to have every single financial transaction in the world be broadcast to everyone and included in the block chain…
Bitcoin backed banks will solve these problems…
Most Bitcoin transactions will occur between banks, to settle net transfers. Bitcoin transactions by private individuals will be as rare as… well, as Bitcoin based purchases are today.”
From the very beginning, many of Bitcoin’s earliest adopters clearly understood its limitations and the resulting downstream implications. What has changed since then? Not the math.
Even with the Lightning Network, an innovation that Hal Finney would not be around to see, the upper limit for the number of regular users Bitcoin can onboard in its current state is optimistically 100 million. That number does not factor in usability/user experience whatsoever, which is an inherent challenge of the Lightning Network due to the very novel way in which it works compared to any other financial system.
In the Lightning Network whitepaper itself, authors Joseph Poon and Thaddeus Dryja make it clear that alone it is not any kind of silver bullet enabling global scale:
“If all transactions using Bitcoin were conducted inside a network of micropayment channels, to enable 7 billion people to make two channels per year with unlimited transactions inside the channel, it would require 133 MB blocks (presuming 500 bytes per transaction and 52560 blocks per year)”
The resulting cap on users who can leverage Bitcoin today in a self sovereign way without the use of a trusted 3rd party presents an obvious problem. Especially if we assume adoption and usage will continue to grow.
Saifdean Ammous authored “The Bitcoin Standard”, a book which received much fanfare for making the compelling economic case for Bitcoin as the ultimate manifestation of “hard money”. A Bitcoin standard, he argues, will out-compete the current fiat money system by virtue of its hard supply. Similarly, in 2014 Pierre Rochard popularized the idea of the “speculative attack”, arguing that the adoption of the bitcoin monetary unit would happen first gradually, then extremely rapidly.
In our projection of the future, we will assume both lines of thinking are correct, and that demand for bitcoin the monetary unit will attract an increasing amount of savings as its network effects only further accelerate its own widespread global adoption.
This “hyperbitcoinization” scenario however presents an impossible challenge for the current constraints of both the Bitcoin core protocol and Lightning Network. What will it mean then when hundreds of millions, and then billions, flee into the confidence of Bitcoin’s fixed supply as the mainstream Bitcoin community believes they will?
Very simply, if they can’t afford to use the core protocol or even the Lightning Network (no need to even discuss ease of use or UX here, that’s a separate sizable challenge) due to hard scalability limits, they will be forced to use centralized and custodial providers. Even if they don’t want to.
There’s no beating around this bush or wishing it away.
If you accept the premise of bitcoin as a superior money, and also understand the practical limitations of the protocol today, then this is the certain outcome Bitcoin is currently on track to reach.
Gold Standard 2.0
It’s a fair question to ask why this might pose a problem at all. Hal Finney certainly didn’t seem to imply so in his own aforementioned post.
Returning to the Bitcoin Standard, Ammous dedicates a significant amount of the book’s opening chapters to discussing the history of the gold standard, its strengths, and most importantly its weaknesses. Crucially he identifies the Achilles heel: Gold was simply too expensive to secure and difficult to transact with in meaningful quantities.
As a result, paper money technology first came to be used as convenient IOUs for gold, which itself was stored in centralized locations specialized to the task of guarding and transferring large amounts of gold as needed. Over time as technology improved and commerce became more global, these centralized custodians only continued to grow, until they were all eventually captured by States through regulatory power and later outright fiat, which completely severed the new fiat money from the underlying gold backing.
In projecting the future for Bitcoin in its current state, we can see a very similar outcome unfolding. There might not be a cost issue with the storage of bitcoin using private keys and mnemonic phrases, but in our hyperbitcoinization scenario the ability to transact with self custodied bitcoin quickly evaporates for all but the institutions and the super wealthy who can afford the fees, even when using Lightning.
The consequences are much the same as they were under a gold standard. Platforms like Coinbase or Cashapp will take center stage, given transactions within their custodial platforms have zero marginal cost as they are just tracked in a central database. Cross platform payments can also be aggregated between these platforms with Lightning channels or on-chain payments extremely cost effectively. The result is a landscape that is not all too dissimilar from the state of the gold standard in the early 20th century, with most supply held by large custodial institutions which States could trivially influence, coerce, and capture.
To return to the question of the biggest threat to Bitcoin: In this future, there’s zero necessity in attacking the base layer if the only ones that can actually use it are large known entities with everything to lose.
To be sure, substantial differences from the original gold standard would in fact exist. Transactions being natively digital, proof of reserves being possible, and the supply being completely transparent are notable improvements over the gold standard. Still, none of these differences impact our self custody conundrum in any way. As far as the vision of Bitcoin being a censorship resistant money, once the vast majority is held by trusted third parties, there is nothing stopping States from strictly enforcing transaction monitoring, asset seizures, and capital controls. There is also nothing stopping them from enabling and even encouraging fractional reserve policies in the interest of prudent economic management.
Crucially, in the event of these actions, the vast majority of users would have no ability to opt out by withdrawing funds to their own custody.
It’s not all bad. In this scenario, bitcoin the monetary unit still appreciates by leaps and bounds. Everyone who’s humored me this far with their attention will still likely stand to financially benefit immensely in this future.
But is that it?
Is the vision of Bitcoin as a foundational tool for censorship resistance, and separating money and State, dead?
If we continue to deny, or worse encourage, the current trajectory, then there’s zero doubt that it is. But it doesn’t have to be.
Misplaced Fear
Fortunately, there’s no reason or prevailing argument for the Bitcoin network to have already ossified. It remains firmly within the grasp of the core community to continue to push forward research, debate, and proposals for further improving the base protocol to increase the scale and usability of solutions like the Lightning Network, as well as enable whole new potential constructs such as the Ark protocol, advanced statechains, and more.
It’s important however, to acknowledge how we’ve reached such a point that “ossification” became a significant prescriptive narrative, rather than a purely descriptive idea of the eventual end state of a widely adopted Bitcoin protocol. Such a prescription is necessarily rooted in the assumption that Bitcoin’s largest attack vector comes from future code changes.
This line of thinking isn’t baseless. It is true that protocol changes can be an attack vector. After all, we’ve actually seen that very attack play out before with Segwit2X when a consortium of large Bitcoin institutions and miners coordinated a unilateral hard fork to the Bitcoin protocol to increase the base block size in 2017.
However we must also acknowledge that Segwit2x failed in a miserable fashion. Worse still, the futility of the attack was obvious before its eventual collapse as it entirely misjudged the dynamics involved in introducing changes to a distributed peer to peer protocol.
The participation of many of the individuals and companies involved with Segwit2X suffered lasting reputational damage in many cases, making it not only a failed effort, but a costly one. For any enterprising attacker looking to compromise Bitcoin for good, it would be abundantly clear that attempting to repeat this approach or any variation of it is a fool’s errand.
A much easier and cheaper approach with a much higher likelihood of success, would be to invest in slowing the already challenging work of building consensus to introduce beneficial extensions to the Bitcoin protocol, ensuring that the experiment in both sound and censorship resistant money is ultimately a victim of its own success. Whether or not you believe this is actively happening today, the actions that need to be taken are identical.
So What Now
Ultimately, where we are now and what we must do is not so different from the time Hal made his observation in 2009: We must continue critically examining the limitations of the Bitcoin protocol and ecosystem, and push forward as a community to address these shortcomings.
Thankfully a number of research advancements and proposals have been made for further increasing scalability that don’t require larger block sizes. Bitcoin core contributor James O’Beirne released a blog post last year with a sober technical analysis of Bitcoin’s immediate scalability prospects and gives good context to some of these proposals, and more recently Mutiny wallet developer Ben Carman has taken a critical look at the issues surrounding the Lightning Network more specifically.
There has never ceased to be a strong signal amidst all the noise, and the best we can do is put in the individual work to identify and amplify it, while actively pushing back against counter productive narratives that do not contribute to meaningfully improving Bitcoin.
By doing that, perhaps we can find a way to scale the vision of truly peer to peer and sovereign money to every single person on the planet.
We may very well still fall short, and there’s absolutely no guarantees.
But it’s worth a shot.
This is a guest post by Ariel Deschapell. Opinions expressed are entirely their own and do not necessarily reflect those of BTC Inc or Bitcoin Magazine.